Functional foods are transforming how we approach what’s on our plate. More than a fleeting trend, these foods are carefully chosen for their ability to nourish the body while delivering specific health benefits. From gut-friendly yogurt to antioxidant-packed berries, functional foods have captured the spotlight for a good reason.
So, what are functional foods exactly? Unlike regular foods that solely provide basic nutrition, functional foods go a step further. They are designed—or naturally equipped—to support your immunity, enhance mental clarity, or even improve heart health. In this article, we’ll explore what makes functional foods powerful, how they’ve shaped diets across history, and why they’re vital in modern wellness.
What Are Functional Foods?
Functional foods are more than just a source of calories—they offer health benefits beyond basic nutrition. These foods contain bioactive compounds, vitamins, or minerals that positively impact your body. For instance, foods rich in antioxidants help combat free radicals, while probiotics support gut health. Functional foods can be naturally occurring, like fruits and vegetables, or fortified, like milk enriched with Vitamin D.
Historically, functional foods have been a cornerstone of traditional diets. Ancient cultures unknowingly embraced these foods for their health-enhancing properties. Fermented foods like kimchi, yogurt, and sauerkraut have been consumed for centuries, not only as a means of preservation but also for their ability to support digestion and immunity. Similarly, turmeric, used in Indian and Ayurvedic practices, was celebrated for its anti-inflammatory benefits.
Functional foods have gained popularity in the health and wellness industry. They are now scientifically studied, marketed, and widely incorporated into everyday diets. From fortified breakfast cereals to adaptogenic teas, modern consumers actively seek functional foods to meet specific health goals like boosting energy, reducing stress, or supporting longevity.
The Benefits of Functional Foods
Functional foods are celebrated for enhancing health in several impactful ways. Here’s a detailed breakdown of their benefits:
Overall Health Improvement
Functional foods play a vital role in improving overall health. For example, probiotics in yogurt and fermented foods support gut health, which is directly linked to better digestion and immunity. Similarly, omega-3 fatty acids from fish or flaxseeds help reduce inflammation, contributing to a balanced immune response. Antioxidant-rich foods like berries combat oxidative stress, which can lead to cell damage and aging.
Disease Prevention
One of the standout benefits of functional foods is their ability to reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Regular consumption of foods like oats (rich in beta-glucans) helps lower cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of heart disease. Similarly, consuming polyphenol-rich foods, such as green tea and dark chocolate, has been associated with a lower risk of diabetes and certain cancers. These foods contain compounds that protect cells from damage, maintain hormonal balance, and improve vascular health.
Enhanced Mental Health
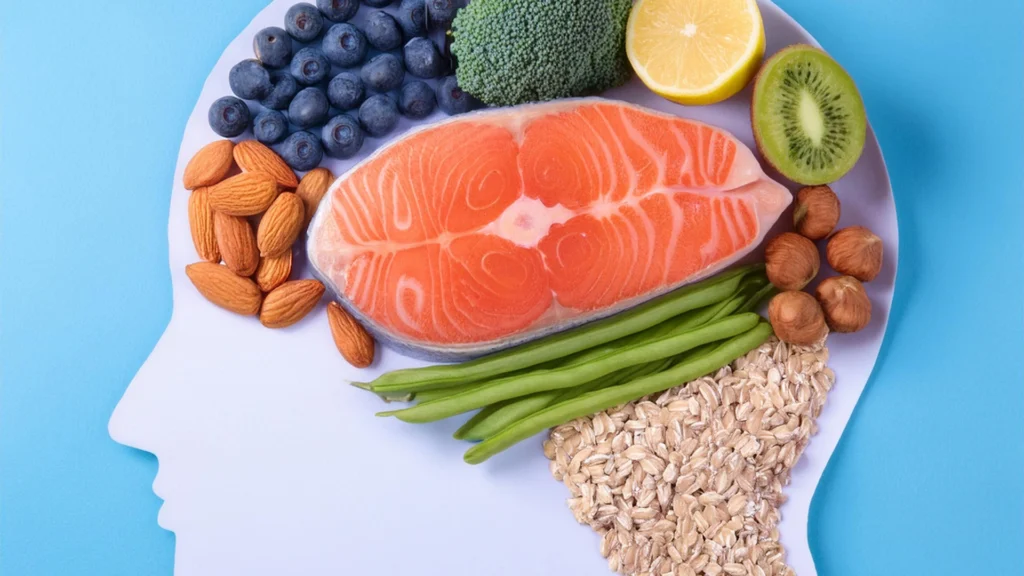
Functional foods can also positively impact mental well-being. Ingredients like omega-3 fatty acids support brain function, improving memory and cognitive abilities. Fermented foods containing probiotics influence gut-brain communication, which can help reduce symptoms of stress and anxiety. Studies have shown that diets rich in these functional foods may lower the risk of mood disorders and enhance overall mental clarity. Additionally, functional medicine doctors often recommend incorporating these foods to manage stress, reduce anxiety naturally, and support emotional balance.
Athletic Performance and Recovery
Functional foods can significantly benefit athletes and fitness enthusiasts. Protein-rich options like eggs, nuts, and legumes aid muscle repair and recovery after exercise. Functional beverages like electrolyte-rich sports drinks or adaptogenic teas boost energy and endurance. Foods rich in nitrates, like beets, improve oxygen delivery to muscles, enhancing stamina during workouts.
Skin and Hair Health
The nutrients in functional foods also extend their benefits to your skin and hair. Collagen-rich foods, or those that stimulate collagen production (such as citrus fruits), can reduce signs of aging. Antioxidants from foods like carrots and sweet potatoes protect the skin from harmful UV rays. Omega-3s and biotin-rich foods, like salmon and walnuts, promote hydrated skin and stronger hair.
Types of Functional Foods
Functional foods come in a variety of forms, ranging from naturally occurring ingredients to scientifically enhanced products. Understanding their types can help you incorporate them into your diet more effectively. Below is an exploration of the major categories:
Naturally Functional Foods
Some foods are naturally rich in nutrients that promote health. These include fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds, which have been a part of healthy diets for centuries.
- Fruits: Berries are loaded with antioxidants that fight free radicals, while citrus fruits provide Vitamin C to boost immunity.
- Vegetables: Leafy greens like spinach and kale are rich in iron and folate, supporting red blood cell production. Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and Brussels sprouts contain compounds linked to cancer prevention.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds are packed with omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, and protein, contributing to heart and brain health.

Fortified or Enriched Foods
Fortified foods have added nutrients that enhance their health benefits. They are especially beneficial for filling nutritional gaps in modern diets.
- Cereals: Breakfast cereals enriched with vitamins and minerals provide essential nutrients like iron, which support energy levels.
- Dairy Products: Many yogurts are fortified with probiotics or calcium, supporting both gut health and bone density.
- Plant-Based Milk: Options like almond or soy milk are often enriched with Vitamin B12, a crucial nutrient for energy and nerve function.
Fermented Foods
Fermented foods are a natural source of probiotics that enhance gut microbiome health. They are an age-old tradition with modern scientific backing. Examples of fermented foods include yogurt, kimchi, sauerkraut, and kombucha are all excellent fermented foods. They help maintain a healthy gut microbiome, influencing digestion, immunity, and mental health.
Functional Beverages
Functional beverages are a convenient way to consume nutrients and functional compounds. They’re gaining popularity as a modern health solution. Some examples of functional beverages are green tea and adaptogenic teas, which are rich in antioxidants and stress-relieving properties. Infused water and sports drinks with electrolytes and vitamins help with hydration and energy recovery.
Supplements and Powders
Supplements and powders are designed for people with specific health or fitness goals. They provide concentrated nutrients in an easy-to-consume form. Protein powders are perfect for muscle repair; greens powders deliver concentrated vegetables, and meal replacements offer balanced nutrition in a convenient package.
Key Ingredients in Functional Foods
Understanding the key ingredients found in functional foods can help you choose those that best support your specific health goals. Here’s a breakdown of the most powerful ingredients and their benefits:
Probiotics and Prebiotics
Probiotics and prebiotics are vital for gut health, which significantly impacts overall well-being. Probiotics are live microorganisms that help maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria, improving digestion and immunity. Prebiotics, on the other hand, are non-digestible fibers that nourish these beneficial bacteria. Foods like yogurt, kimchi, and other fermented products are rich in probiotics, while bananas, garlic, and onions are good sources of prebiotics. Together, they support a balanced microbiome, aiding digestion, reducing inflammation, and even influencing mental health.
Antioxidants
Antioxidants are powerful compounds that protect the body from oxidative stress, which can lead to cell damage, aging, and various diseases. By neutralizing free radicals, antioxidants help reduce the risk of chronic conditions such as heart disease, cancer, and diabetes. Berries like blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are rich in antioxidants, as are dark chocolate, green tea, and certain nuts. These foods are delicious and effectively defend against the damage caused by environmental toxins and the natural aging process.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats that play a key role in supporting heart health, brain function, and skin hydration. These healthy fats help reduce inflammation, improve blood flow, and support cognitive function. Omega-3s are found in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines and in plant-based sources such as flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. Regular consumption of omega-3-rich foods has been linked to a lower risk of heart disease, improved brain health, and better skin elasticity, making them an essential part of a balanced diet.
Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamins and minerals are crucial for various bodily functions, and many functional foods are fortified with additional nutrients to support specific health needs. For example, calcium and Vitamin D are essential for bone health, while Vitamin C boosts immunity and helps with skin regeneration. Many plant-based milk products, cereals, and dairy foods are enriched with these vitamins and minerals to ensure that people receive adequate nutrition, especially when dietary intake may be insufficient. Regularly consuming fortified foods can help prevent nutrient deficiencies and promote overall health.
Phytochemicals
Phytochemicals are natural compounds found in plant-based foods that have been shown to reduce the risk of disease. These include flavonoids, carotenoids, and polyphenols, which offer antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer properties. For instance, flavonoids found in tea can reduce the risk of heart disease, while resveratrol in grapes may protect against age-related diseases. Consuming a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables, such as tomatoes, spinach, and berries, ensures a rich intake of these powerful plant compounds.
Adaptogens
Adaptogens are natural substances that help the body adapt to stress and restore balance. These ingredients, such as ashwagandha, reishi mushrooms, and holy basil, have been used in traditional medicine for centuries. They are believed to regulate the body’s stress response, enhance energy levels, and promote a sense of calm. Incorporating adaptogens into your diet through functional foods like adaptogenic teas, powders, and supplements can help manage the effects of stress and support emotional and physical resilience. This is particularly beneficial for those looking to reduce anxiety naturally, as adaptogens help stabilize the body’s response to stress.
How to Incorporate Functional Foods into Your Diet

Start by adding antioxidant-rich foods like berries, spinach, or tomatoes to your meals. These can be easily incorporated into smoothies, salads, or toppings on your morning oatmeal. To boost gut health, make yogurt or kefir a part of your daily breakfast or snack routine, as these fermented foods are full of probiotics that support digestion and immunity. For heart health, include omega-3-rich foods like salmon, walnuts, or flaxseeds a few times a week. You can add flaxseeds to smoothies, sprinkle them on yogurt, or use them as a topping for your morning cereal.
A great way to enhance your beverages is to swap out regular tea for green tea or adaptogenic teas, which help manage stress while providing antioxidants. If you’re not fond of drinking green tea, you can also incorporate functional beverages like kombucha into your routine for added probiotics and digestive benefits.
When aiming for a healthier diet overall, consider replacing refined grains with whole grains, which provide fiber and additional nutrients. For example, opt for quinoa or oats instead of white rice or processed cereals.
Functional Foods and Specific Health Goals
Functional foods can be tailored to meet specific health goals, from weight loss to enhancing energy and mental clarity. Here’s how certain functional foods can help you achieve your health objectives:
Functional Foods for Weight Loss
When it comes to weight loss, functional foods can play an essential role by promoting satiety, boosting metabolism, and reducing cravings. Foods high in fiber, like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, slow down digestion and keep you feeling fuller longer. Protein-rich foods like lean meats, legumes, and nuts contribute to weight loss by reducing hunger and boosting metabolism. Functional foods like green tea and chili peppers, which contain metabolism-boosting compounds like catechins and capsaicin, can increase calorie burn and promote fat loss. This ties into functional medicine for weight loss, where dietary interventions and specific foods help individuals reach their goals efficiently.
Functional Foods for Heart Health
For heart health, functional foods that lower cholesterol, improve circulation, and reduce inflammation are essential. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish like salmon, are well-known for reducing blood triglyceride levels and preventing plaque buildup in arteries. Foods like oats, beans, and nuts are also high in soluble fiber, which helps lower bad cholesterol (LDL). Antioxidant-rich foods like berries and dark chocolate can protect blood vessels from oxidative stress. Regularly consuming these heart-healthy foods and incorporating plant-based options like leafy greens will help maintain a healthy heart and improve overall cardiovascular health.
Functional Foods for Energy and Endurance
For sustained energy and endurance, functional foods can be a game-changer. Whole grains like quinoa and oats provide slow-releasing energy, while nuts and seeds deliver healthy fats that fuel the body throughout the day. Foods rich in iron, such as spinach and beans, improve muscle oxygen delivery, enhancing endurance during physical activity.
Additionally, foods like bananas, sweet potatoes, and dark chocolate are rich in potassium and magnesium, which help prevent muscle cramps and fatigue. To ensure optimal energy levels, consuming a variety of functional foods that replenish your energy stores and support muscle recovery after exercise is important.
Functional Foods for Mental Clarity
Integrating functional foods that support brain health can improve mental clarity and focus. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, have been shown to enhance cognitive function and reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases. Antioxidant-rich foods like blueberries, spinach, and dark chocolate protect brain cells from oxidative damage and help improve memory.
For stress management, adaptogens like ashwagandha and reishi mushrooms can help regulate the body’s stress response and promote mental calmness. Including these foods in your daily routine can boost concentration, reduce mental fatigue, and enhance overall cognitive health. Functional medicine for mental health also uses these types of foods to improve mood and mental clarity naturally.
Potential Risks and Considerations
While functional foods offer numerous health benefits, it’s important to consider potential risks and ensure that their incorporation into your diet is balanced and appropriate for your needs. Overconsumption of certain functional foods, especially fortified ones, may lead to an excess of specific nutrients, which could have negative health effects. For example, excessive intake of fortified vitamins or minerals can cause toxicity or disrupt the balance of other nutrients in the body. Similarly, some functional foods, such as those containing high amounts of caffeine or adaptogens, may interfere with sleep or lead to overstimulation if consumed in large quantities.
People with certain medical conditions or those taking specific medications should be cautious when adding functional foods to their diet. For instance, individuals on blood thinners should be careful with foods rich in vitamin K (like leafy greens) as they could interfere with medication effectiveness. Additionally, some fermented foods, while beneficial for gut health, can cause digestive issues for individuals with sensitivities or conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
As with any dietary change, moderation is key. Functional foods should complement a well-rounded diet and not replace essential nutrients from whole foods. Consulting with a nutritionist or healthcare provider can help ensure that functional foods are included safely, especially for those with specific health goals or conditions.
Conclusion
Incorporating functional foods into your diet offers a powerful way to improve your health and well-being. The benefits are wide-ranging and scientifically backed, from enhancing digestion and boosting immunity to supporting mental clarity and heart health. Adding functional foods such as antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and probiotics to your meals can support various aspects of your health and achieve specific health goals.
However, it’s important to remember that while functional foods can significantly improve health, they should be part of a balanced diet. Moderation and variety are crucial to avoid overconsumption of certain nutrients or ingredients. By choosing functional foods thoughtfully and understanding their unique benefits, you can enjoy better health while supporting your long-term wellness goals.